MIGS Glaucoma Surgery: A Safer, More Effective Way to Manage Glaucoma
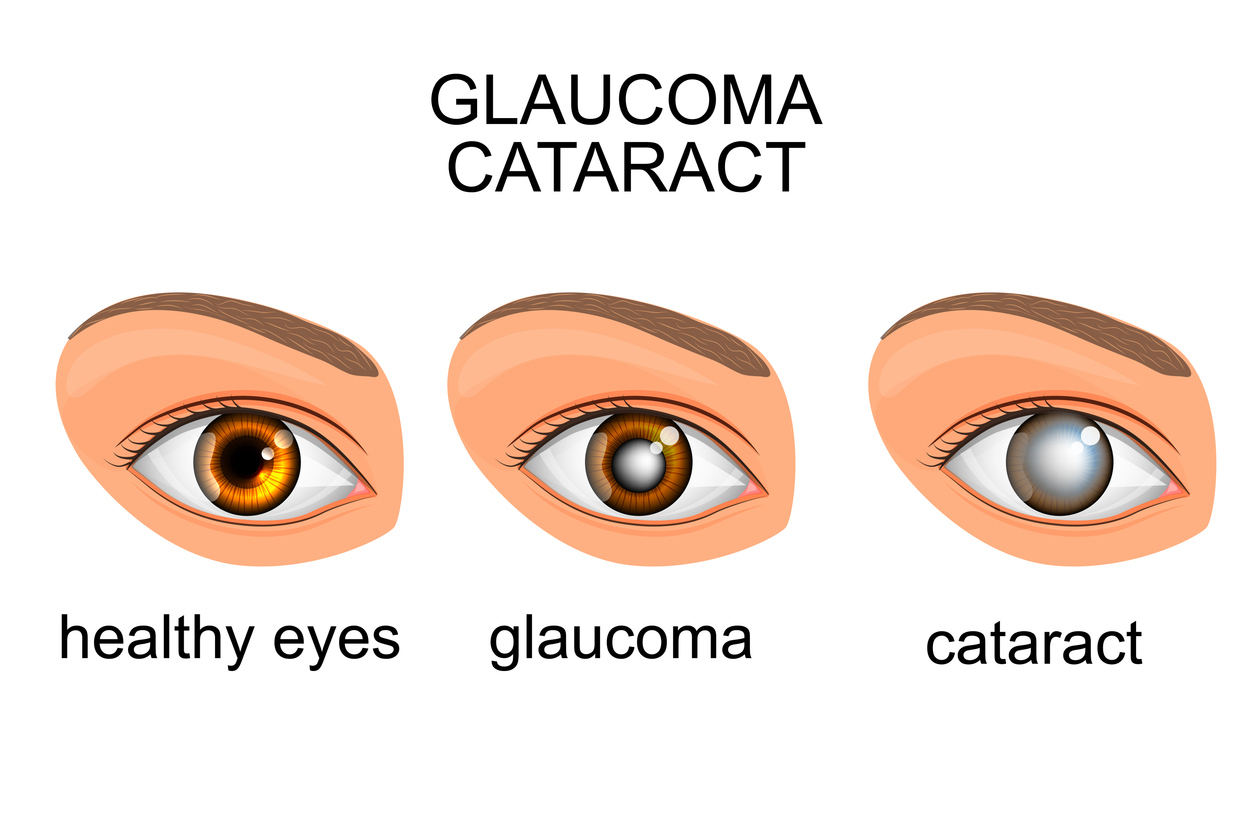
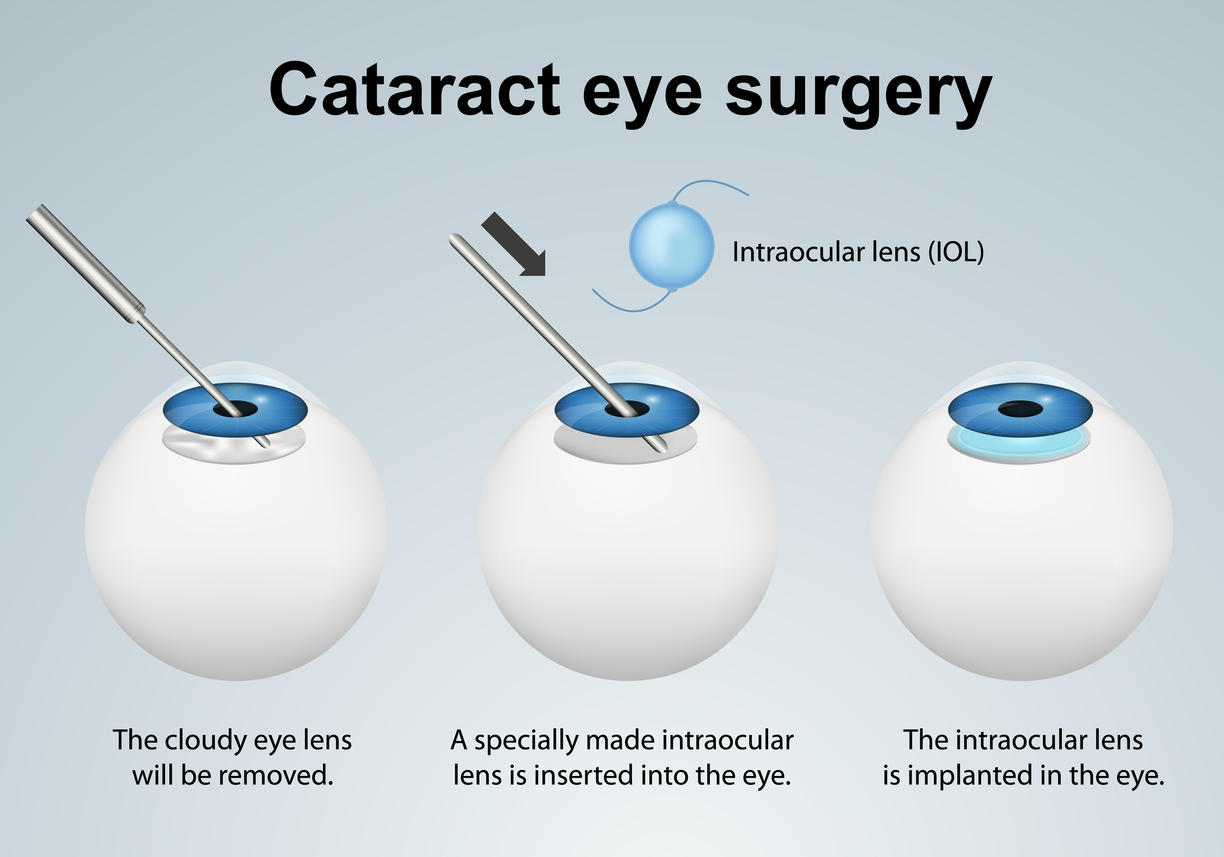
MIGS, or Minimally Invasive Glaucoma Surgery, is a cutting-edge treatment designed to reduce intraocular pressure (IOP) in patients with glaucoma. Unlike traditional glaucoma surgery, MIGS uses tiny incisions and advanced devices to improve fluid drainage in the eye, protecting the optic nerve from further damage. This procedure is often performed alongside cataract surgery and is ideal for patients with mild-to-moderate glaucoma.
For those looking for an effective solution with shorter recovery times and fewer complications, MIGS offers a safer alternative to more invasive glaucoma surgeries. Read on to explore how MIGS works, who it benefits, and why it’s transforming glaucoma care.
MIGS vs. Traditional Glaucoma Surgery: Key Differences
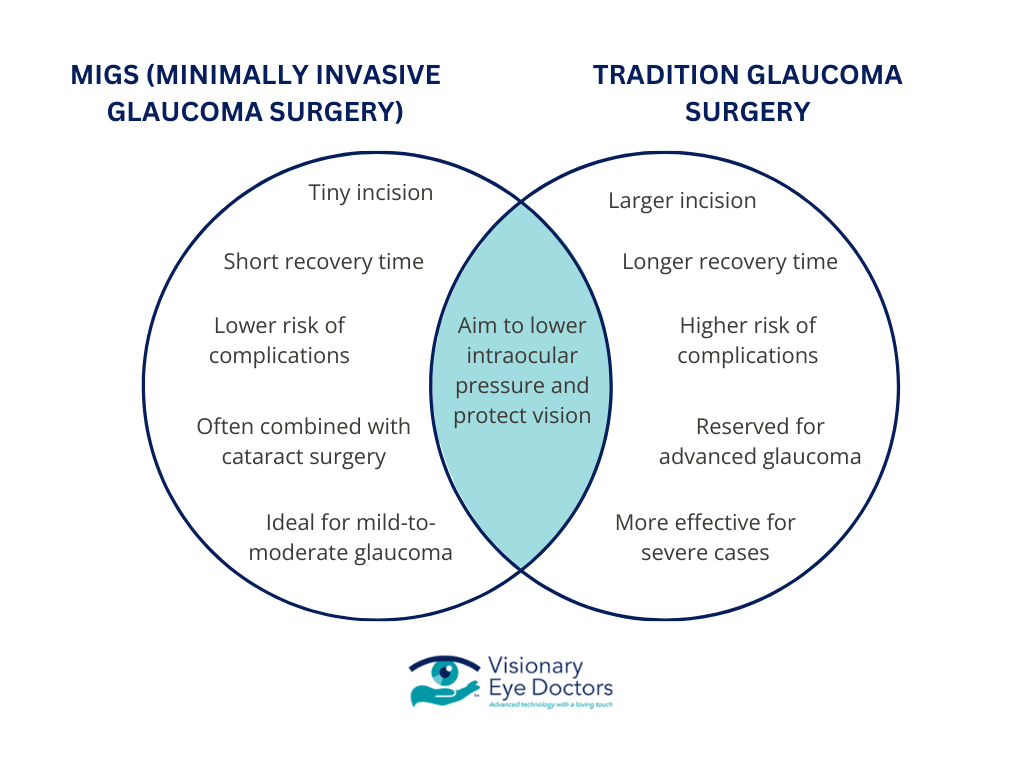
Minimally Invasive Glaucoma Surgery (MIGS) stands apart from traditional glaucoma surgeries like trabeculectomy and tube shunt surgery in several significant ways. Here’s how:
Less Invasive Approach
- MIGS utilizes a tiny incision and advanced devices, such as the iStent inject® or Hydrus Microstent, to enhance fluid drainage.
- This approach minimizes trauma to the eye’s delicate structures, particularly the trabecular meshwork and Schlemm’s canal, compared to traditional surgeries.
Faster Recovery Time
- The minimally invasive nature of MIGS means patients often experience shorter recovery times, allowing them to resume daily activities more quickly than with traditional glaucoma surgery.
Improved Safety Profile
- MIGS has a significantly lower risk of complications. It avoids the long-term issues sometimes associated with more invasive glaucoma surgeries, such as infection or scarring.
Combination with Cataract Surgery
- MIGS is frequently performed during cataract surgery, providing dual benefits for patients who require both glaucoma and cataract treatment. This streamlined approach enhances overall outcomes and reduces the need for multiple surgeries.
Ideal for Mild-to-Moderate Glaucoma
- While traditional surgeries are often reserved for advanced glaucoma cases, MIGS is well-suited for patients with open-angle glaucoma or early-stage disease.
By offering a safer, faster, and more effective alternative, MIGS is reshaping the way glaucoma is managed, making it a preferred choice for many patients seeking to lower intraocular pressure and protect their vision.

The MIGS Procedure: Steps and Technology
MIGS (Minimally Invasive Glaucoma Surgery) utilizes advanced techniques and devices to lower intraocular pressure (IOP) by improving the flow of aqueous humor, the fluid inside the eye. Here’s a closer look at how it works:
1. Devices Used in MIGS
- iStent inject®: The smallest FDA-approved medical device, implanted to create tiny bypasses in the trabecular meshwork, enhancing fluid drainage into Schlemm’s canal.
- Hydrus Microstent: A flexible microstent placed in Schlemm’s canal to increase aqueous outflow.
- Xen Gel Stent: A soft tube shunt that creates a new drainage pathway to reduce eye pressure.
- Kahook Dual Blade: A surgical tool that removes part of the trabecular meshwork, improving fluid outflow naturally.
2. Surgical Procedure
- The MIGS procedure is performed under local anesthesia and involves a tiny incision in the anterior chamber of the eye.
- Using specialized devices, the surgeon enhances or bypasses the natural drainage system to improve fluid drainage and reduce IOP.
- The surgery is quick, often taking only a few minutes, with minimal discomfort for the patient.
3. How MIGS Reduces Eye Pressure
- By targeting the trabecular meshwork or Schlemm’s canal, MIGS restores the eye’s natural ability to drain aqueous humor.
- This continuous outflow helps prevent the buildup of fluid that causes optic nerve damage and vision loss.
4. Combination with Cataract Surgery
- MIGS can be performed alongside cataract surgery, making it an efficient option for patients needing treatment for both conditions. During cataract surgery, MIGS devices can be implanted seamlessly, enhancing overall outcomes.
MIGS represents a significant advancement in glaucoma care, offering patients a less invasive and more effective way to manage their condition while minimizing risks and recovery time.
Is MIGS Glaucoma Surgery Right for You?
MIGS (Minimally Invasive Glaucoma Surgery) is a versatile treatment option designed for patients with specific needs. While it offers numerous benefits, it may not be suitable for everyone. Here’s what you need to know about who can benefit from this innovative surgical approach:
Ideal Candidates
- Open-Angle Glaucoma Patients: MIGS is most effective for individuals with mild-to-moderate open-angle glaucoma, the most common type of glaucoma.
- Patients Undergoing Cataract Surgery: MIGS can be performed in combination with cataract surgery, offering dual benefits of vision correction and IOP reduction.
- Those Who Struggle with Glaucoma Medication: If daily eye drops or other medical therapies are ineffective or difficult to maintain, MIGS can provide a more consistent and reliable solution.
When MIGS May Not Be Suitable
- Advanced Glaucoma Cases: Patients with severe glaucoma or significant optic nerve damage may require more traditional or invasive surgical options.
- Angle-Closure Glaucoma: MIGS is less effective for this type of glaucoma, which involves a different mechanism of increased eye pressure.
Why Consult a Glaucoma Specialist?
Every patient’s condition is unique. A glaucoma specialist can assess your specific needs, including the severity of your glaucoma, your response to medical therapy, and your overall eye health. They can recommend whether MIGS or another treatment option is the best course of action for managing your condition.
MIGS is a promising option for many individuals, offering a safer, less invasive alternative to traditional surgeries. If you fit the criteria for MIGS, it could be a life-changing solution for maintaining your vision and reducing the burden of ongoing treatments.

Expert Care for MIGS Glaucoma Surgery at Visionary Eye Doctors
At Visionary Eye Doctors, our team of highly trained glaucoma specialists provides advanced, patient-focused care for managing glaucoma with innovative procedures like MIGS. Our experienced doctors, including Dr. Reena Garg and Dr. Georgina Medina, specialize in the most effective treatment options to preserve your vision and improve your quality of life.
We utilize the latest FDA-approved MIGS devices, including the iStent inject® and Hydrus Microstent, to ensure the best possible outcomes. Whether you’re exploring surgical options or managing glaucoma with eye drops, our tailored approach is designed to meet your specific needs.
If you’re considering MIGS, it’s essential to work with specialists who understand your condition and the available options. At Visionary Eye Doctors, we offer:
- Comprehensive glaucoma evaluations, including visual field testing and imaging with OCT technology.
- Expertise in combining MIGS with cataract surgery for patients with dual needs.
- Access to cutting-edge diagnostics and a full spectrum of glaucoma treatment options.
Schedule an appointment today to learn more about MIGS and whether it’s the right solution for your glaucoma. Visit us to begin your journey toward better vision with trusted care from Visionary Eye Doctors.